Professor, Pharmacology and Toxicology
Degrees and Appointments
- B.S. 1989, Hertford College, University of Oxford
- Ph.D. 1992, Hertford College, University of Oxford
- Postdoctoral Fellow 1992-1994, University of Texas, Austin
- Research Fellow 1994-1999, RPR, Collegeville PAHead HTMC 1999-2004, Amgen, Thousand Oaks, CA
Fields of Study: Organic Chemistry, Drug Discovery/Medicinal Chemistry
Research Specialities: Chemical Biology, Synthesis/Synthetic Methods Development
Awards and Honors:
- Abbott Labs New Faculty Award, 2007
Research
The Hulme group is located at BIO5 Oro Valley Drug Discovery Center and is focused on small molecule drug design and developing enabling chemical methodologies to expedite the drug discovery process. The development of small molecule inhibitors of kinases is of particular interest. Projects are highly collaborative in nature, and students are exposed to the full array of design hurdles involved in progressing molecules along the value chain to clinical evaluation.
1. THERAPIES FOR ALZHEIMER'S AND NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASES
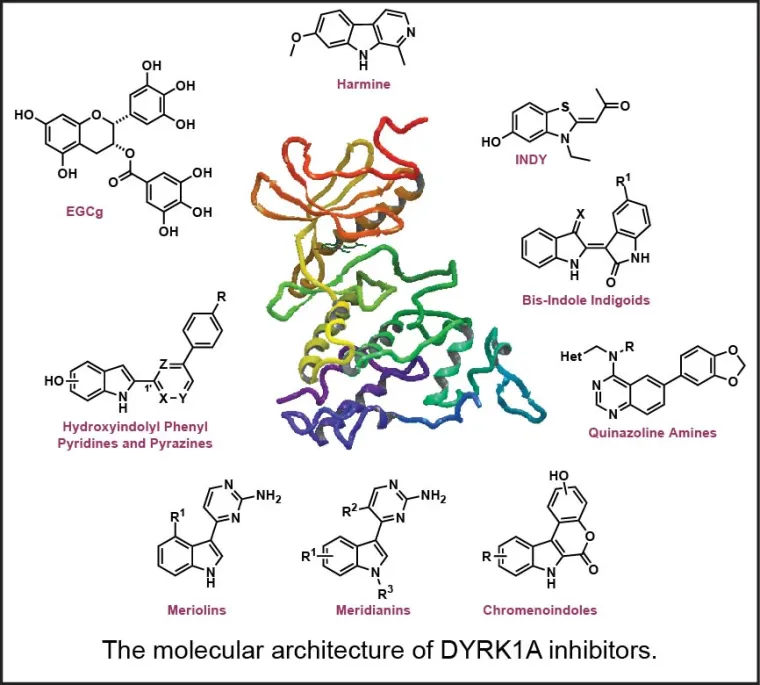
With 24.3 million people affected in 2005 and an estimated rise to 45 million in 2020, dementia is currently a leading unmet medical need and a costly burden on public health. Seventy percent of these cases have been attributed to Alzheimer's disease (AD), a neurodegenerative pathology whose most evident symptom is a progressive decline in cognitive functions. Studies in the group focus on providing a significant mechanistic alternative to common approaches that solely focus on small molecule design toward APP-cleavage inhibition. In particular, ongoing efforts are aimed at the design of structurally novel small molecule inhibitors of the dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A (DYRK1A) and their evaluation of in vivo activity and measurement of in vivo tau phosphorylation and neurofibrillary tangles pathology in 3X-TgAD mouse models of AD. Moreover, DYRK1A has also been suggested to affect other cellular pathways that may be involved in mental impairment and neurodegenerative dementia.
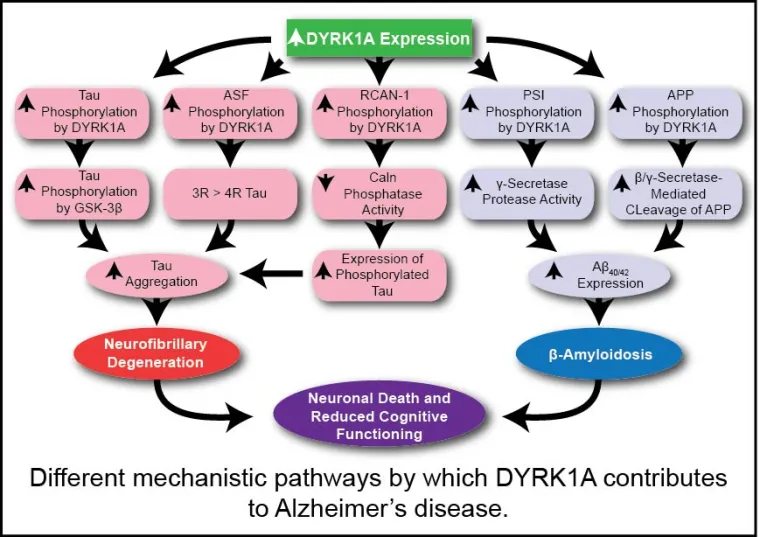
Studies are being conducted with a long-term collaborator (Dr. Travis Dunckley) at Translational Genomics (TGen). Inhibition of DYRK1A functioning should theoretically mitigate multiple processes underlying the progression of neurodegeneration, particularly in the AD-related therapeutic area, for which key DYRK1A substrates include: (1) tau protein, (2) amyloid precursor protein, and (3) presenilin 1 (the catalytic subunit of γ-secretase), all pointing to clear mechanisms through which elevated DYRK1A activity may be promoting AD progression. Several other AD-related kinases are targets of current interest in the group (Smith B, Medda F, Gokhale V, Dunckley T, Hulme C [2012] Recent Advances in the Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Selective DYRK1A Inhibitors: A New Avenue for a Disease Modifying Treatment of Alzheimer's? ACS Chem. Neurosci., DOI: 10.1021/cn300094k).
2. THERAPEUTICS MODULATING PROSTAGLANDIN E2 PRODUCTION
Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) is well known to play a pivotal role in processes associated with inflammation, pain, and pyresis and is over-expressed in various tumors where chronic inflammation has been linked to the growth of various cancerous tissues. Indeed, PGE2 has been identified as the major prostaglandin associated with the progression of various tumor malignancies, including that of the colon, lung, and breast. An ongoing project within the group is the development of novel small molecules that mitigate PGE2 production and display antitumor growth properties in vivo . Several novel series of small molecules have been developed and are under further investigation (Smith B, Chang HH, Medda F, Gokhale V, Dietrich J, Davis A, Meuillet EJ, Hulme C [2012] Synthesis and biological activity of 2-aminothiazoles as novel inhibitors of PGE2 production in cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 22:3567-3570).
3. ENABLING CHEMICAL METHODOLOGIES
A. APPLICATIONS OF MULTI-COMPONENT REACTIONS
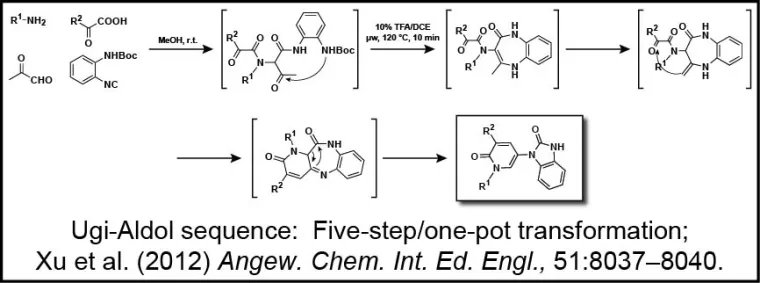
The group also has a long-standing interest in the development of new reactions that produce biologically relevant molecules in an efficient manner. Indeed, front-loading screening collections with molecules possessing high "iterative efficiency potential" is critical for expediting the drug discovery process. Compounds derived from multi-component reactions (MCRs) demonstrate such potential, and thus their discovery and applications are of utmost importance. Closely linked with the Molecular Libraries Small Molecule Repository, the group seeks to develop operationally friendly chemistry that delivers products of high molecular diversity that ultimately enable library production and deposition of compounds in both national and local screening collections. A one-pot five-step transformation developed in the group is depicted (Xu Z, De Moliner F, Cappelli A, Hulme C [2012] Ugi/Aldol Sequence: Expeditious Entry to Several Families of Densely Substituted Nitrogen Heterocycles. Angewandte Chem., Int. Ed., 51:8037-8040).
Recent discoveries in the group have facilitated a new project toward the expeditious syntheses and application of novel dendrimer families, repetitively branched molecules that show high promise in drug delivery, gene delivery, and sensor technologies.
B. NEW HYPERVALENT IODINE METHODOLOGY AND APPLICATIONS
Novel hypervalent iodine-mediated C-H activation methodologies and their application for the preparation of novel peptidomimetics are an active area of research.
C. ORGANOSELENIUM CHEMISTRY
A recent discovery of a new selenium dioxide-mediated oxidative amidation is driving new studies in molecular diversity generation.
De Molinera F, Hulme C (2012) A Van Leusen deprotection-cyclization strategy as a fast entry into two imidazoquinoxaline families. Tetrahedron Lett., 53:5787-5790.
Smith B, Medda F, Gokhale V, Dunckley T, Hulme C (2012) Recent advances in the design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of selective DYRK1A inhibitors: a new avenue for a disease modifying treatment of Alzheimer's? ACS Chem. Neurosci. DOI: 10.1021/cn300094k.
Medda F, Hulme C (2012) A facile and rapid route for the synthesis of novel 1,5-substituted tetrazole hydantoins and thiohydantoins via a TMSN3-Ugi/RNCX cyclization. Tetrahedron Lett., 53:5593-5596.
Chen YH, Lu PJ, Hulme C, Shaw AY (2012) Synthesis of kojic acid-derived copper-chelating apoptosis inducing agents. Med. Chem. Res. DOI 10.1007/s00044-012-0094-y.
Xu Z, De Moliner F, Cappelli A, Hulme C (2012) Ugi/Aldol sequence: expeditious entry to several families of densely substituted nitrogen heterocycles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., 51:8037-8040.
Sells E, Medda F, Chang H, Gokhale V, Hulme C, Meuillet EJ (2012) Abstract 2834: Discovery of a novel class of prostaglandin e2 synthesis inhibitors with anti-tumor activity in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res., 72:1.
Xu Z, Shaw AY, Nichol GS, Cappelli AP, Hulme C (2012) Applications of ortho-phenylisonitrile and ortho-N-Boc aniline for the two-step preparation of novel bis-heterocyclic chemotypes. Mol. Divers., 16:607-612.
Gunawan S, Keck K, Laetsch A, Hulme C (2012) Synthesis of peptidomimetics, d- and e-lactam tetrazoles. Mol. Divers., 16:601-606.
Ayaz, M, De Moliner F, Dietrich J, Hulme C (2012) Applications of isocyanides in IMCRs for the rapid generation of molecular diversity. In "Isocyanide Chemistry"; Nenajdenko, V. Ed. Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany; pp. 335-384.
Xu Z, Ayaz M, Cappelli A, Hulme C (2012) A general one-pot, two-step protocol accessing a range of novel polycyclic heterocycles with high skeletal diversity. ACS Comb. Sci., 14:460-464. [Congrats also on getting the cover!]
Shaw AY, Denning CR, Hulme C (2012) Selenium dioxide-mediated synthesis of a-ketoamides from arylglyoxals and secondary amines. Tetrahedron Lett., 53:4151-4153.
Xu Z, Shaw AY, Dietrich J, Cappelli AP, Nichol G, Hulme C (2012) Facile, novel two-step syntheses of benzimidazoles, bis-benzimidazoles, and bis-benzimidazole-dihydroquinoxalines. Mol. Divers., 16:73-79.
Gunawan S, Ayaz M, De Moliner F, Frett B, Kaiser C, Patrick N, Xu Z, Hulme C (2012) Synthesis of tetrazolo-fused benzodiazepines and benzodiazepinones by a two-step protocol using an Ugi-azide reaction for initial diversity generation. Tetrahedron, 68:5606-5611.
Smith B, Chang HH, Medda F, Gokhale V, Dietrich J, Davis A, Meuillet EJ, Hulme C (2012) Synthesis and biological activity of 2-aminothiazoles as novel inhibitors of PGE2 production in cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 22:3567-3570.
Shaw AY, McLaren JA, Nichol GS, Hulme C (2012) Hydrazine-mediated cyclization of Ugi products to synthesize novel 3-hydroxypyrazoles. Tetrahedron Lett., 53:2592-2594.
Shaw AY, Xu Z, Hulme C (2012) Ugi/Robinson-Gabriel reactions directed toward the synthesis of 2,4,5-trisubstituted oxazoles. Tetrahedron Lett., 53:1998-2000.
Shaw AY, Medda F, Hulme C (2012) Facile and rapid route for the synthesis of novel norstatine analogs via PADAM-cyclization methodology. Tetrahedron Lett., 53:1313-1315.
De Moliner F, Hulme C (2012) Straightforward assembly of phenylimidazoquinoxalines via a one-pot two-step MCR process. Organic Lett., 14:1354-1357.
Gunawan S, Petit J, Hulme C (2012) Concise one-pot preparation of unique bis-pyrrolidinone tetrazoles. ACS Comb. Sci., 14:160-163.
Gunawan S, Nichol G, Hulme C (2012) Concise route to a series of novel 3-(tetrazol-5-yl)quinoxalin-2(1H)-ones. Tetrahedron Lett., 53:1664-1667.
Roberts SA, Martinez-Ariza G, Dietrich J, Hulme C (2012) 2,4-Diphenyl-6-trifluoro-methyl-2,3-dihydro-1H,5H-pyrrolo-[3,4-c]pyrrole-1,3-dione. Acta Crystallogr. Sec. E: Struct. Rep. Online:E68.2:o496-o497.
Ayaz M, Dietrich J, Hulme C (2011) A novel route to synthesize libraries of quinoxalines via Petasis methodology in two synthetic operations. Tetrahedron Lett., 52:4821-4823.
Dömling A, Hulme C (2011) Editorial in "Special issue on Mini-MCR issue and SCS-09 - Second International Symposium on Combinatorial Sciences in Biology, Chemistry, Catalysts and Materials." Mol. Divers., 15:1-2.
Gunawan S, Nichol GS, Chappeta S, Dietrich J, Hulme C (2011) Concise preparation of novel tricyclic chemotypes: fused hydantoin-benzodiazepines. Tetrahedron Lett., 51:4689-4692.
Xu ZG, Dietrich J, Shaw AY, Hulme C (2010) Two-step syntheses of fused quinoxaline-benzodiazepines and bis-benzodiazepines. Tetrahedron Lett., 51:4566-4569.
Dietrich J, Hulme C, Hurley LH (2010) The design, synthesis, and evaluation of 8 hybrid DFG-out allosteric kinase inhibitors: a structural analysis of the binding interactions of Gleevec®, Nexavar®, and BIRB-796. Bioorg. Med. Chem., 18:5738-5748.
Dietrich J, Kaiser C, Meurice N, Hulme C (2010) Concise two-step solution phase syntheses of four novel dihydroquinazoline scaffolds. Tetrahedron Lett., 51:3951-3955.
Meurice N, Wang L, Lipinski CA, Yang ZB, Hulme C, Loftus JC (2010) Structural conservation in band 4.1, ezrin, radixin, moesin (FERM) domains as a guide to identify inhibitors of the proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2. J. Med. Chem., 53:669-677.
Hulme C, Chappeta S, Dietrich J (2009) A simple, cheap alternative to designer convertible isonitriles' expedited with microwaves. Tetrahedron Lett., 50:4054-4057.
Hulme C, Dietrich J (2009) Emerging molecular diversity from the intra-molecular Ugi reaction: iterative efficiency in medicinal chemistry. Mol. Divers., 13:195-207.
Hulme C, Chappeta S, Griffith C, Lee YS, Dietrich J (2009) An efficient solution phase synthesis of triazadibenzoazulenones: 'designer isonitrile free' methodology enabled by microwaves. Tetrahedron Lett., 50:1939-1942.
Hulme C, Lee YS (2008) Emerging approaches for the syntheses of bicyclic imidazo[1,2-x]-heterocycles. Mol. Divers., 12:1-15.
Hulme C, Maggiora GM (2008) Molecular diversity: from small to large, emerging to enabling. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 12:257-259.
Umkehrer M, Ross G, Jager N, Burdack C, Kolb J, Hu H, Alvini-Gaston M, Hulme C (2007) Expeditious synthesis of imidazo[1,2-c]pyrimidines via a [4+1]-cycloaddition. Tetrahedron Lett., 48:2213-2216.
Masquelin T, Bui H, Brickley B, Stephenson G, Schwerkoske J, Hulme C (2006) Sequential Ugi/Strecker reactions via microwave assisted organic synthesis: novel 3-center-4-component and 3-center-5-component multi-component reactions. Tetrahedron Lett., 47:2989-2991.
Ma V, Bannon AW, Baumgartner J, Hale C, Hsieh F, Hulme C, Rorrer K, Salon J, Van Staden C, Tempest P (2006) Solid-phase synthesis and structure-activity relationships of novel biarylethers as melanin-concentrating hormone receptor-1 antagonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 16:5066-5072.
Salamant W, Hulme C (2006) Unique one step, multicomponent a,β,β-oxidations of carbamates with Willgerodt-like hypervalent iodine reagents - an example of triple C-H bond activation. Tetrahedron Lett., 47:605-609.






